Summary of screw air compressor rotor fault knowledge, bookmarked!
Rotor components
The rotor components are composed of active rotor (male rotor), driven rotor (female rotor), main bearing, thrust bearing, bearing gland, balance piston and balance piston sleeve.
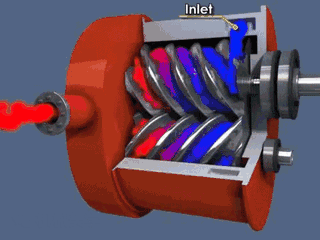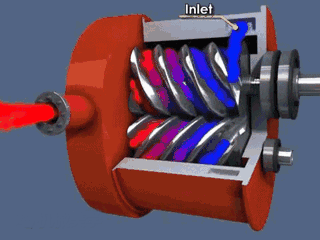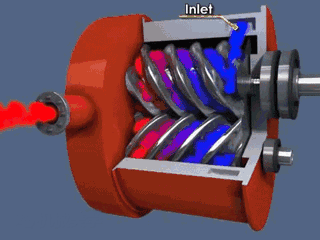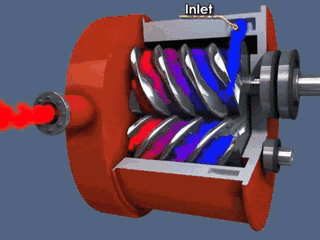
Common fault phenomena of male and female rotors
1. Normal mechanical wear and aging.
● The outer diameter of the male and female teeth of the rotor is worn.
● Normal wear of the rotor cylinder.
2. Man-made mechanical damage
● Scratches on the outer diameter of the male and female rotor tooth tracks.
● Scratches on the rotor cylinder.
● Scratches on the sides of rotor intake and exhaust end covers.
● The wear of the bearings at the intake and exhaust ends and the wear of the inner circle of the bearing cover.
● Wear of shaft diameter at rotor bearing location.
● The shaft ends of the male and female rotors are deformed.
3. Abraded or stuck general parts
● Scratches and seizures (occlusion) between the female and male rotors.
● Between the outer diameter of the rotor and the inner wall of the machine body.
● Between the exhaust end face of the rotor and the exhaust bearing seat.
● Between the journal of the suction end of the rotor and the shaft hole of the machine body.
● Between the journal of the exhaust end of the rotor and the shaft hole of the exhaust bearing housing.
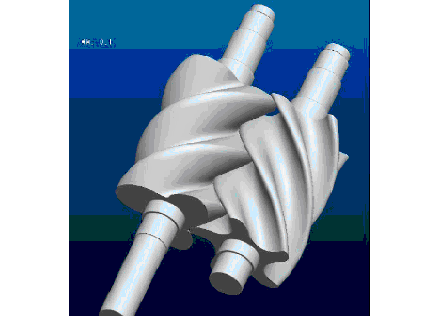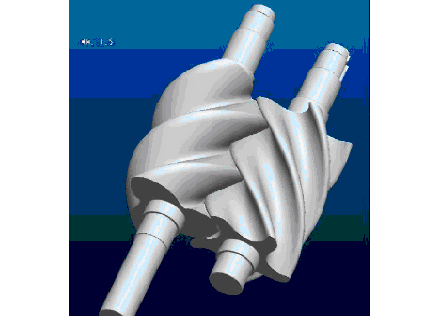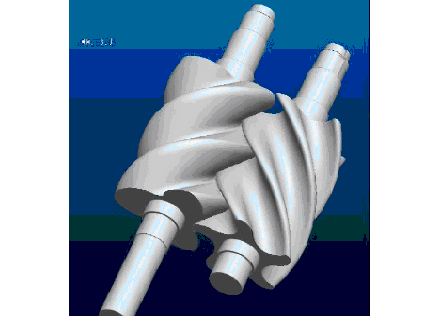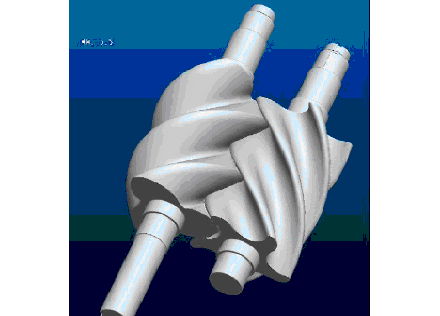
Cause of issue
1. The air filter element is not replaced in time, resulting in poor intake air quality and severe rotor wear; the mixed use of different brands of lubricating oil will often lead to interaction and wear of the rotor;
2. The type of compressor oil used is unqualified or not replaced in time according to the regulations, and the impurities in the oil exceed the standard, resulting in scratches on the rotor and cylinder;
3. Exhaust temperature is too low during operation, resulting in excessive moisture in the oil and gas. Long-term operation will cause oil emulsification, resulting in long-term operation so that the bearings at the intake and exhaust ends cannot be effectively lubricated during high-speed and heavy-load rotation. And the heat is damaged, causing the rotor to be skewed, deformed and stuck;
4. Due to the meshing clearance of the driving coupling gear or the failure of the gear key connection, the shaft head of the rotor driving end is deformed;
5. Abnormal damage caused by bearing quality. The above failures of the air compressor are generally caused by human beings. In the daily inspection and maintenance work, as long as the operation and maintenance are carefully followed the operation and maintenance procedures, the above faults can be completely avoided.
In short, the suction and discharge end journals of the screw compressor rotor are supported by the bearings on the compressor body and the exhaust bearing seat respectively. If the coaxiality of the compressor body, exhaust bearing seat and rotor is due to mechanical processing or assembly If the design requirements are not met, it is easy to cause scratches between the rotors, between the rotor and the body, between the rotor and other parts, or the rotor is stuck. Generally, the coaxiality between the shaft hole and the rotor compression chamber is required to be within 0.01-0.02mm.
The gap between the parts in the compression chamber of the screw compressor is generally in the unit of wire or mm. The parts in the compression chamber are dynamic fit. If the designed gap value is too small, coupled with the error in the manufacturing process, it is easy to cause the rotor to be damaged. Scuffing or jamming. The gap between the rotor and the body is generally about 0.1mm, and the gap between the exhaust end surface of the rotor and the exhaust bearing seat is 0.05-0.1mm.
During the disassembly process of the compressor, because the bearing and the rotor shaft are closely matched, if the disassembly force is too large, the parts will be deformed, and the coaxiality of the parts themselves will be reduced.
After the compressor is assembled, it is necessary to check the overall coaxiality of the assembly. If the coaxiality is out of tolerance, it will cause scratches between parts or the rotor will be stuck.
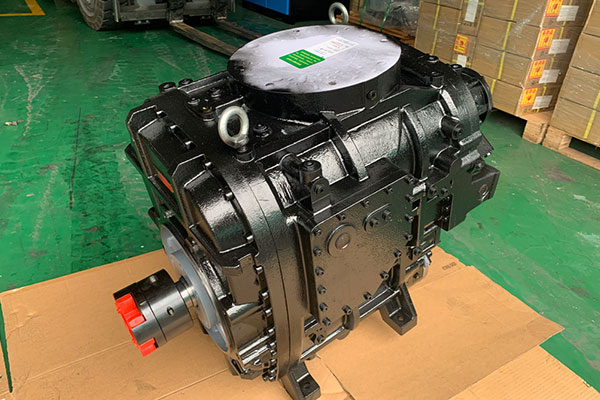

Hazards and Detection of Rotor Damage
During the normal operation of the air compressor, if the sound is abnormal, the vibration becomes larger, the exhaust temperature is too high for a long time, and the current is overloaded, it must be stopped for serious inspection. Focus on checking whether the bearings of the air compressor are damaged and whether the end of the rotor shaft is deformed. If the damage to the rotor end bearing can be detected in time and the machine is shut down immediately, it will not cause the bearing to heat up and get stuck, and will not cause damage to large mechanical parts. If the damage to the rotor end bearing cannot be found in time, and the air compressor runs for a long time, under normal circumstances, there will be friction and sliding between the inner circle of the bearing and the position where the rotor is installed. The outer circle of the bearing rotates due to the jamming of the inner circle of the bearing of the cover, so that the bearing hole of the end cover becomes larger or out of round. There may even be a direct deformation of the rotor under the action of high power due to bearing damage, which will destroy the coaxiality of the rotor.

The detection of male and female rotors generally depends on the wear and scratches of the rotor, and its meshing wear should not be less than 0.5mm-0.7mm of the nominal diameter. The scratch area shall not be greater than 25mm2, the depth shall not be greater than 1.5mm, and the misalignment of the rotor shaft end shall not be greater than 0.010mm.